Corneal ulcers in children
Related content
It is vital to recognise and urgently treat corneal ulcers in children, as they can lead to permanent vision impairment. Children with corneal ulcers due to vitamin A deficiency also have an extremely high risk of mortality.
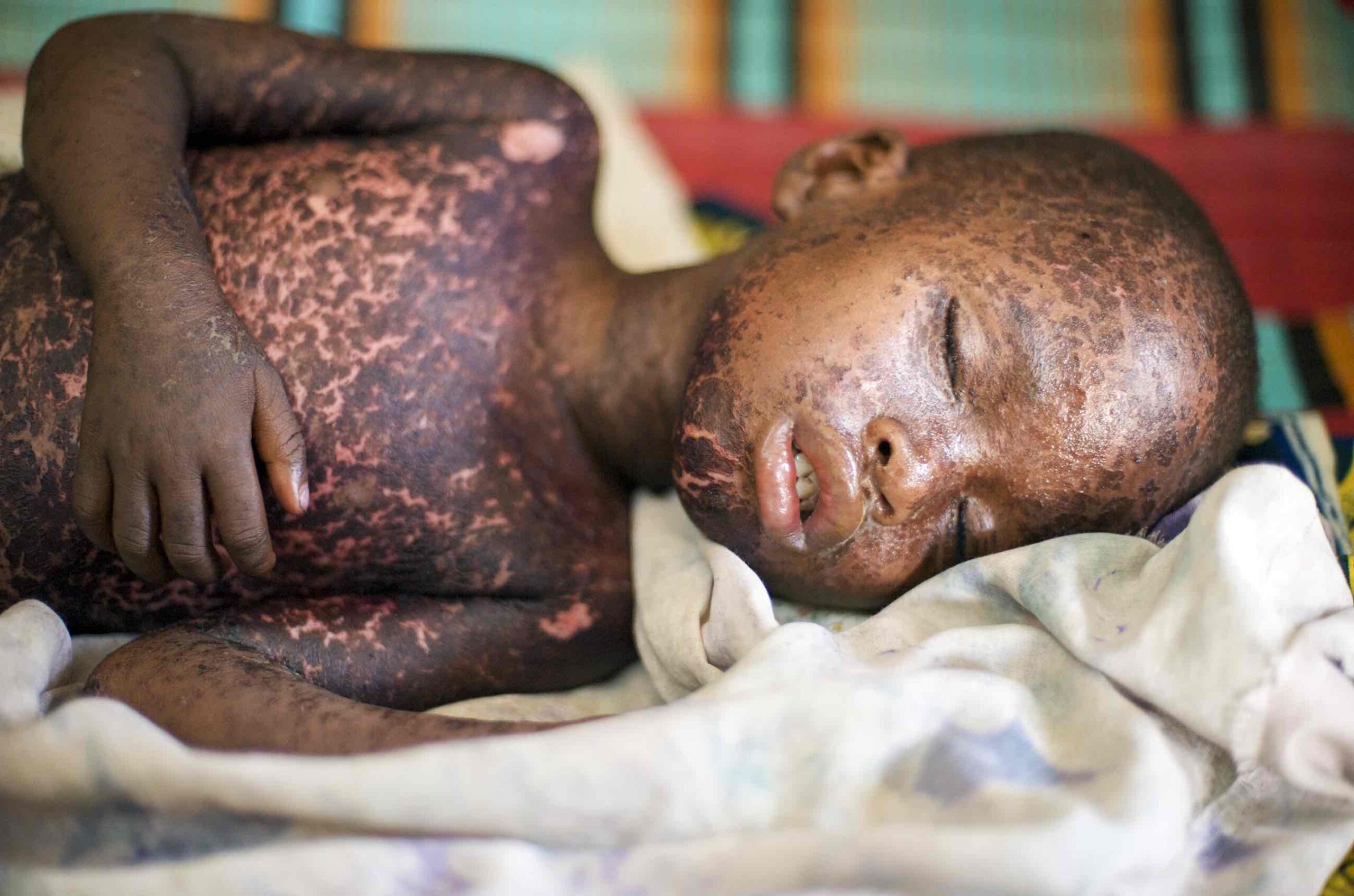
Although corneal ulcers can affect people of all ages, it is particularly important to recognise and treat them urgently in children, as ulcers can lead to scarring and complications that may impair a child’s vision permanently. Children with corneal ulcers due to severe vitamin A deficiency are not only at risk of impaired vision, but also have an extremely high mortality rate: 60% are likely to die within 3 months, unless they are treated.
Other causes of corneal ulcers include injury/trauma, use of harmful remedies, autoimmune conditions, and infections due to viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa. In this article, we focus on causes that are specific to children. For more information on managing corneal ulcers that affect people at any age, including those caused by bacteria and fungi, visit the Community Eye Health Journal online (www.cehjournal.org) and use the search function.
What to look for and do at community/primary level
Red eye and suspected corneal ulcer
Red eyes are common in children, and most resolve with appropriate care. However, the presence of one or more of these signs suggest that a child has developed a corneal ulcer and needs urgent treatment:
• The eye is watering excessively
• The child shows signs of being in pain
• The child shows signs of being sensitive to light
• The child can see less well (measurable as a decrease in visual acuity).
What to do: Immediately refer these children to an eye department where there is an ophthalmologist. If the child is up to 1 month of age, and has swelling of the eyelids as well as profuse, purulent discharge, this could be conjunctivitis of the newborn due to gonococcal infection. Administer intramuscular antibiotics, if available (ceftriaxone 25–50 mg/kg, up to a maximum of 125 mg), and refer the child urgently.
Vitamin A deficiency
Corneal ulcers due to vitamin A deficiency do not always cause a red eye, and are not painful (they may cause discomfort, however, and the child may keep their eyes closed). Suspect corneal ulcers due to vitamin A deficiency if:
• There is a recent or current history of fever, measles, or diarrhoea
• Both eyes are affected.
What to do: Immediately administer high-dose vitamin A (retinyl palmitate) and refer the child to a hospital. Follow up in 24 hours to ensure they are getting the help they need.
The recommended dose for each age group is:
• < 6 months of age: 50,000 international units (IU)
• 6–12 months: 100,000 IU
• > 1 year: 150,000 IU
Children must receive three doses of vitamin A: on day 1, day 2, and day 14.
Diagnosis and management in the eye department
The table below lists the most common causes of corneal ulcers in children, alongside the age typically affected, the organism responsible (if any), and the history, diagnosis, and management of each condition.
Prevention of corneal ulcers in children
Many of the causes of corneal ulcers in children can be prevented as follows:
1. Ocular prophylaxis of the newborn (cleaning the eyelids immediately after birth and instilling a topical antibiotic or antiseptic
2. Measles immunisation and vitamin A supplementation.
3. Good hand hygiene and avoiding getting water in the eyes of contact lens wearers.
4. Preventing the use of harmful eye remedies, which requires measures such as health education and improved access to eye care services.

References
1. Jagadesh C. Reddy, Sayan Basu, Ujwala S. Saboo, Somasheila I. Murthy, Pravin K. Vaddavalli, Virender S. Sangwan, Management, Clinical Outcomes, and Complications of Shield Ulcers in Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis. Am J Ophthamol 2013 155: 550-559.
2. Giuseppe Varacalli, Antonio Di Zazzo, Tommaso Mori, Thomas H. Dohlman, Sara Spelta, Marco Coassin et al. Challenges in Acanthamoeba Keratitis: A Review. J Clin Med 2021 10(5): 942.
